Understanding XRF Analyzers: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s fast-paced world, accurate and non-destructive testing of materials is critical in various industries, from jewelry to aerospace. One of the most effective tools for this purpose is the XRF analyzer. But what exactly is an XRF analyzer, and how does it work? In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of XRF technology, its applications, and why it has become a staple in material analysis.
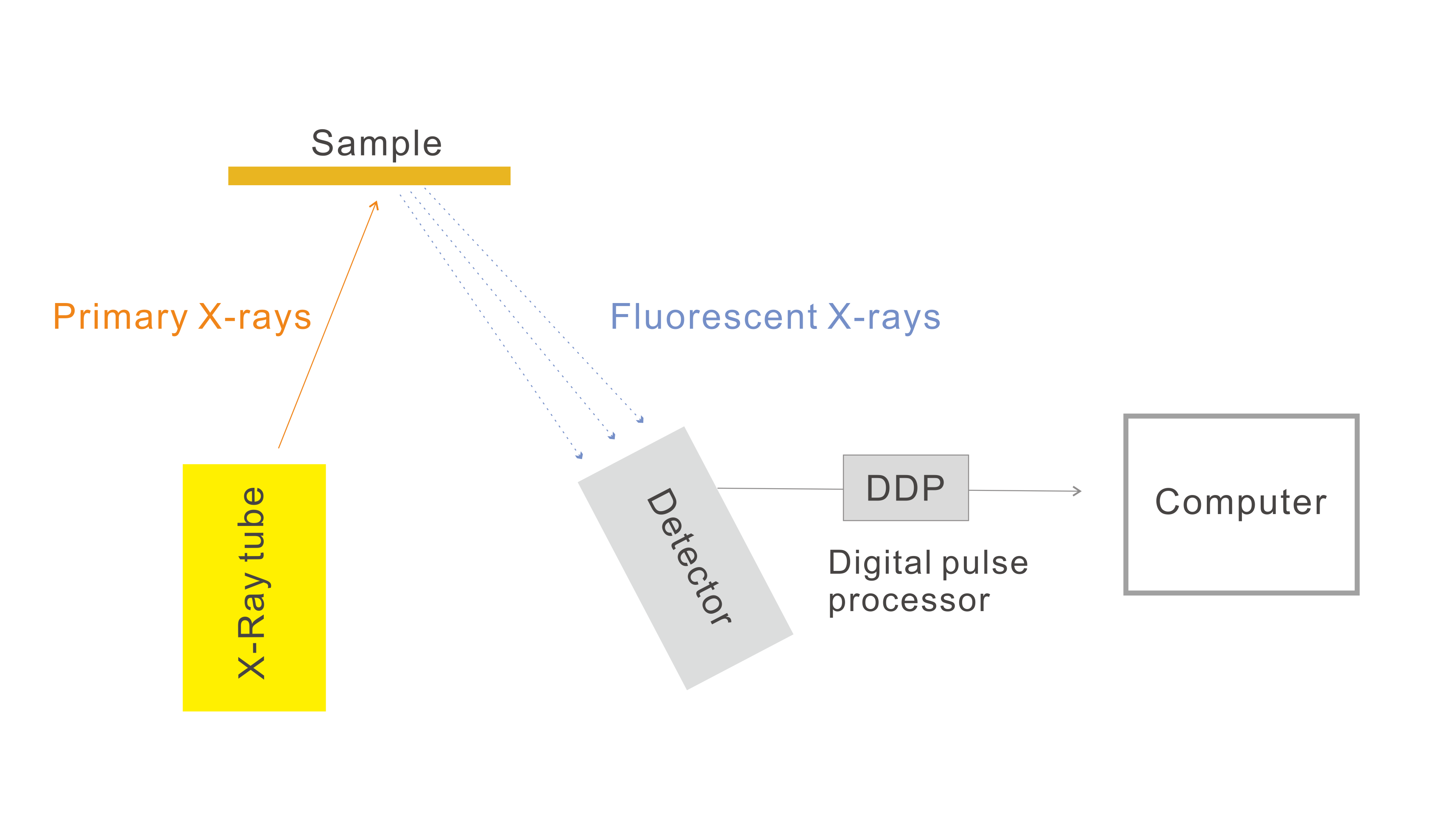
What is an XRF Analyzer?
XRF stands for X-ray fluorescence, a non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. An XRF analyzer is a device that utilizes this technique to identify and quantify the elements within a sample. It’s a versatile tool used in various industries, including metal manufacturing, jewelry, electronics, environmental science, and more.
How Does XRF Technology Work?
The core principle behind XRF technology is the interaction between X-rays and matter. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1. X-ray Emission: The analyzer emits high-energy X-rays towards the sample.
2. Interaction with the Sample: These X-rays interact with the atoms in the sample, causing them to emit secondary X-rays, known as fluorescent X-rays. Each element emits X-rays at a specific energy level, which acts like a fingerprint for that element.
3. Detection: The analyzer’s detector captures these fluorescent X-rays and measures their energy levels.
4. Data Analysis: The analyzer processes this data to identify the elements present in the sample and quantify their concentrations.
Types of XRF Analyzers
XRF analyzers come in various forms, each designed for specific applications:
1. Handheld XRF Analyzers: Compact and portable, these devices are ideal for on-site testing, such as in mining, scrap metal recycling, or quality control in manufacturing. An example is the VR-H5 handheld XRF analyzer, known for its precision in precious metals analysis.
2. Benchtop XRF Analyzers: These are larger, more powerful machines used in laboratories or industrial settings where higher accuracy and detailed analysis are required. Models like the VR-T5 and VR-T6 benchtop XRF analyzers are popular choices, offering fast test speeds and high accuracy.

3. Specialized XRF Analyzers: Some XRF analyzers are designed for specific tasks, such as the VR-X5 gold analyzer, which can test up to 20 elements in precious metals, or the XF-P3 XRF coating thickness analyzer, which measures both the value and coating thickness of materials.
Applications of XRF Analyzers
The versatility of XRF analyzers makes them invaluable in many fields:
– Jewelry and Precious Metals: Jewelers use XRF analyzers to authenticate precious metals and determine their purity without damaging the item. This is especially crucial in buying and selling gold, silver, and platinum.
– Environmental Testing: XRF technology is used to detect pollutants in soil, water, and air, helping to monitor environmental contamination and ensure regulatory compliance.
– Manufacturing and Quality Control: In industries like aerospace and automotive, XRF analyzers ensure that the materials used meet strict quality standards, preventing failures and ensuring safety.
– Archaeology and Art Conservation: XRF analyzers help historians and conservators analyze artifacts and artworks, providing insights into their composition and helping to preserve them.
Advantages of Using XRF Analyzers
– Non-Destructive Testing: One of the biggest advantages of XRF analyzers is that they do not damage the sample. This is especially important in fields like jewelry, where preserving the integrity of the item is crucial.
– Speed and Efficiency: XRF analysis is quick, often providing results in just a few seconds. This speed is essential in high-throughput environments where time is of the essence.
– Accuracy and Precision: Modern XRF analyzers, like the VR-T9, offer accuracy levels that can reach as high as 0.001%, ensuring reliable results.
– Portability: Handheld XRF analyzers allow for on-the-spot testing, making them invaluable in fieldwork and on-site inspections.
Conclusion
XRF analyzers have revolutionized the way industries approach material analysis, offering a fast, accurate, and non-destructive method to determine the elemental composition of a wide range of materials. Whether in a laboratory, a manufacturing plant, or out in the field, these versatile tools are essential for ensuring quality, safety, and authenticity.
As XRF technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly find even more applications, further solidifying its role as a cornerstone of modern material analysis.
If you’re considering investing in an XRF analyzer, it’s essential to choose a model that suits your specific needs. Whether you need a handheld device for fieldwork or a benchtop analyzer for detailed lab analysis, understanding the capabilities and advantages of each type will help you make an informed decision.
 VRAY Instrument Limited
VRAY Instrument Limited